Atlas Overview¶
The Open Source Framework for AI-Driven Community Platforms and Personal Agents
Overview¶
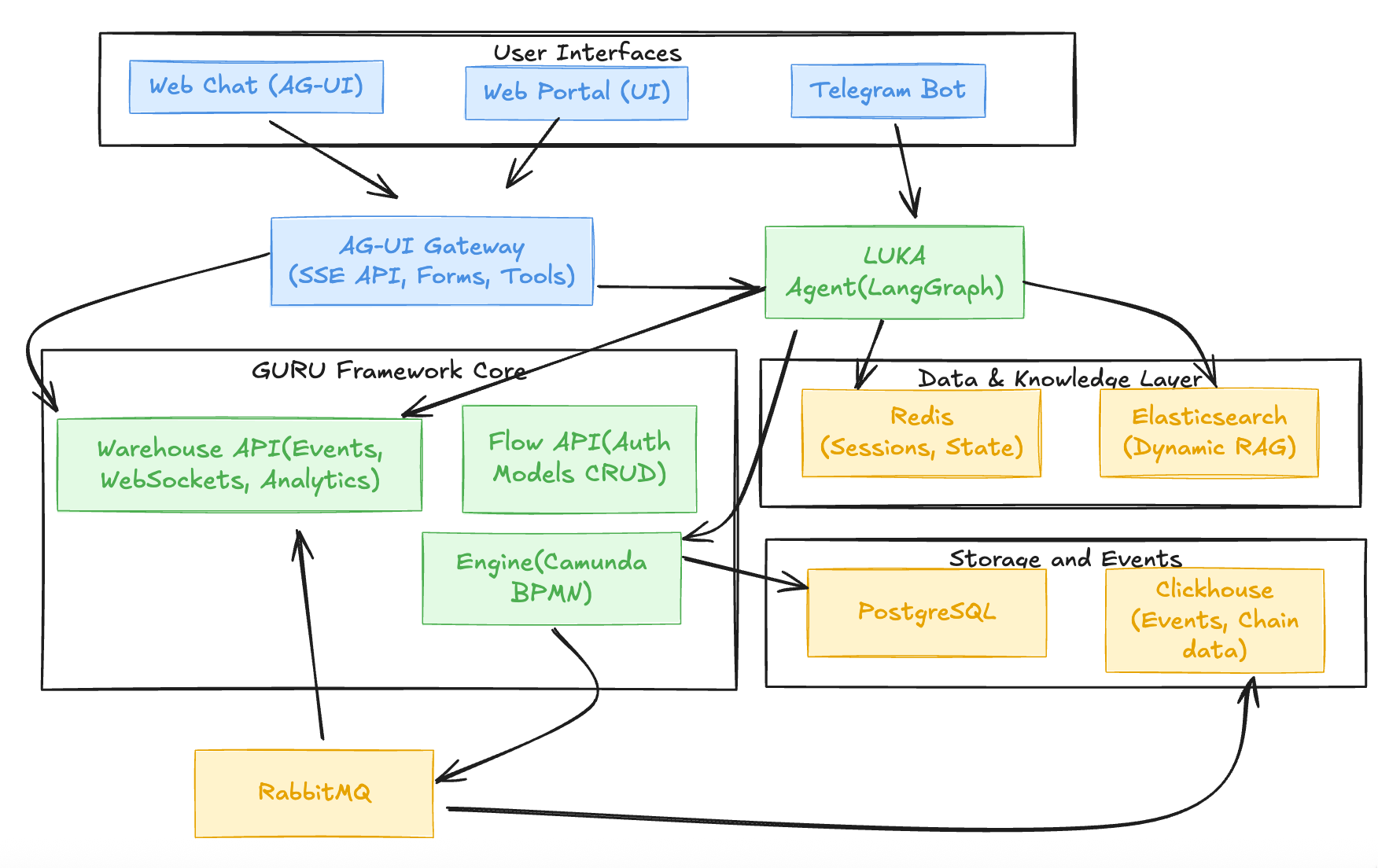
Atlas is an open-source framework that transforms how communities and individuals interact with AI agents, knowledge bases, and automated workflows. Built on battle-tested infrastructure (GURU Framework, Camunda BPMN, LangGraph), Atlas provides:
- Dynamic RAG - Self-propelling knowledge bases from streamed data (Telegram groups, channels, documents)
- Intercom-Style Assistant - Open-source support layer connecting web and Telegram
- Agentic Workflows - Comprehensive scenarios with forms, tools, and business process automation
- One-Click Deployment - Launcher wizard that spins up complete applications in Kubernetes namespaces
Atlas bridges the gap between simple chatbots and enterprise-grade automation, making sophisticated AI agents accessible to everyone.
1. Value Proposition¶
The Problem¶
Most AI assistants today are either:
- Too simple - One-shot prompts with no memory, context, or business logic
- Too complex - Enterprise platforms requiring months of integration and custom development
- Too siloed - Separate systems for local, web, Telegram, knowledge bases, and workflows
The Solution¶
Atlas provides a complete system for building AI-driven applications that:
- Learn continuously from streamed data (messages, documents, events)
- Have comprehensive sub-agents, tools, and structure - Multi-agent systems with specialized capabilities
- Work across interfaces (web, Telegram, API) with shared context
- Execute business logic through rendered BPMN workflows and agentic scenarios
- Deploy in minutes via the launcher wizard, then customize from your fork
Core Value¶
Atlas is not just a chatbot framework - it's a complete orchestration platform where:
- Knowledge bases are dynamic (self-updating from live sources)
- Agents have personas, skills, and contexts (not just prompts)
- Workflows are comprehensive (driving users through pre-set scenarios with conditions, forks, and tools)
- Infrastructure is portable (fork the repo, switch to your own infra, keep developing)
2. Use Cases¶
2.1 Open Source Intercom for Your Service¶
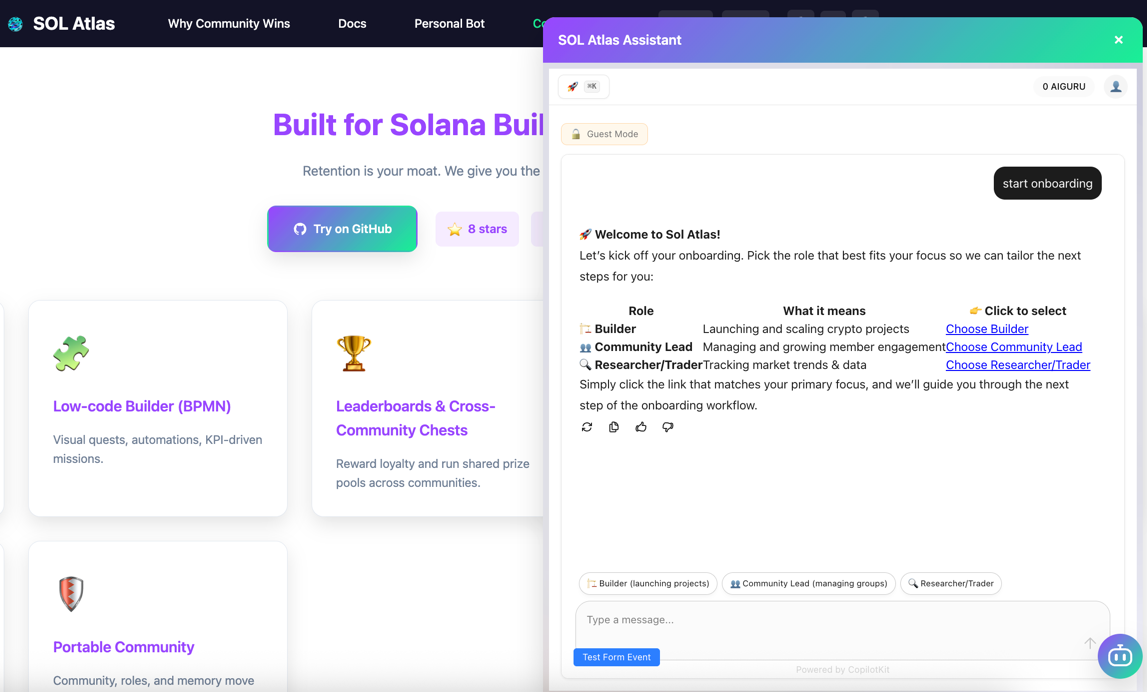
The Use Case: Layer 0-1 support assistant embedded on your landing page or service, connected to your Telegram support group.
How It Works:
- Webchatbot (AG-UI Protocol compatible) embedded on your site
- Connects to AG-UI Gateway (SSE API) for real-time responses
- Works as a Layer 0 AI agent with dynamic self-propelling knowledge base from FAQs and group responses
- Escalates to Telegram support group with full context
- Admins respond in Telegram; replies delivered back to user in web chat
Value:
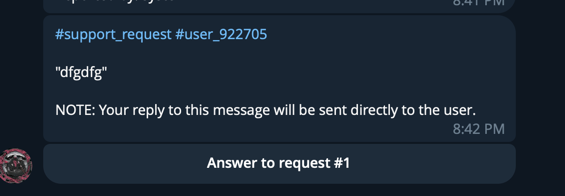
- Deflect support tickets with intelligent, contextual answers
- Unified support across web and Telegram
- No vendor lock-in (open source, self-hosted)
Example: DexGuru uses Atlas webchatbot to answer DeFi questions, route to support when needed, and surface on-chain data panels.
2.2 Chatbot with Comprehensive Workflows¶
The Use Case: Web/Telegram chat bot interface that guides users through complex scenarios (onboarding, quests, transactions) with forms, buttons, and conditional logic.
How It Works:
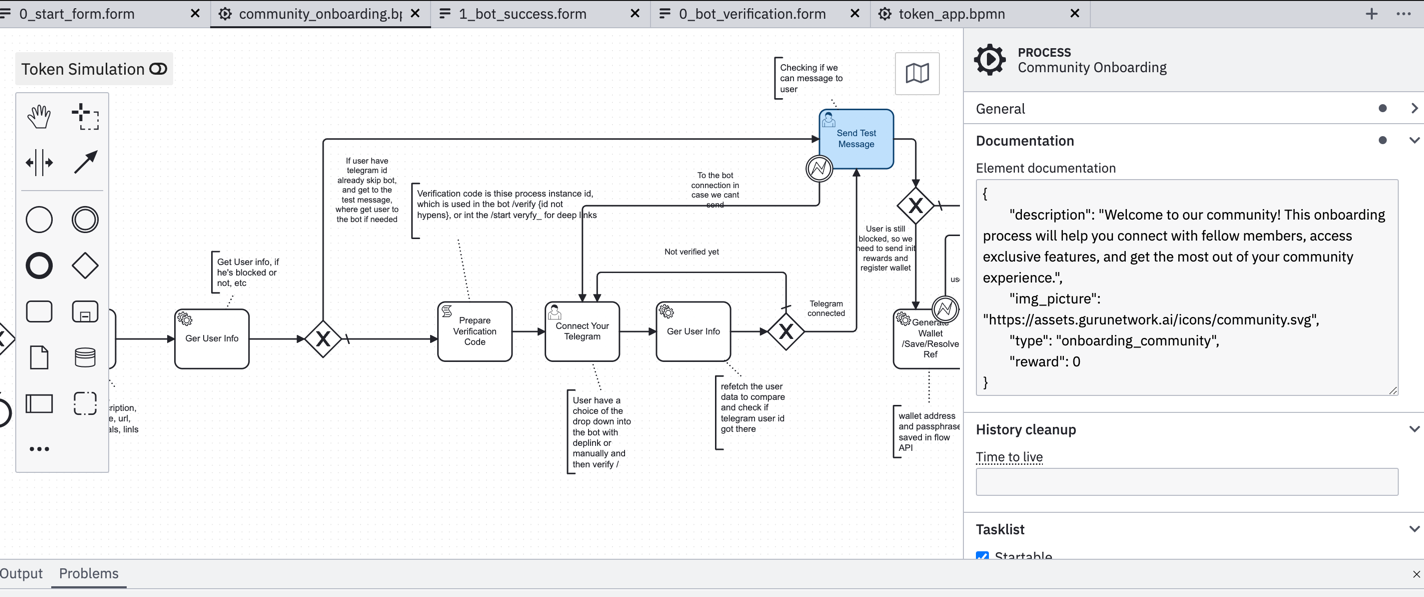
- BPMN workflows define user journeys (visual diagrams or text/YAML) — Example BPMN | Example Forms
- Forms engine (Camunda) renders interactive forms in bot and web
- Sub-agents — Specialized agents with distinct roles, tools, and contexts work together in multi-agent systems
- LLM personas (Context.md + YAML) customize agent behavior - Example Workflow with config.yaml
- Task lists orchestrate user, LLM, and automated actions asynchronously
Value:
- Predictable, testable user experiences (not just "prompt and hope")
- Rich interactions (forms, buttons, inline keyboards, generated interfaces)
- Business logic in sub agentic and BPMN workflows (not buried in code)
Example: Trip Planner bot creates trip artifacts through multi-step workflows; DexGuru scenarios drive users to token swaps with CTAs.
2.3 Gamification & Community Engagement¶
The Use Case: Quest systems, leaderboards, and achievement tracking that drive engagement and retention.
How It Works:
- Quest workflows (BPMN) define missions with conditions and rewards
- Leaderboards(example) track points, badges, and rankings
- Cross-community competitions via Atlas Network
- Wallet integration for token gating and rewards
Value:
- Turn passive followers into active contributors
- Measure and reward engagement
- Network effects across communities
Example: Burning Meme (50K+ channel, 1K+ bot) uses high-frequency quests and hype loops to drive memecoin launches.
2.4 Community Knowledge Management¶
The Use Case: Self-propelling knowledge bases from Telegram groups and channels, with scheduled digests and on-demand answers.
How It Works:
- Dynamic RAG — Streamed messages from groups/channels → Elasticsearch → searchable knowledge base
- Scheduled LLM requests generate digests ("what you missed" recaps)
- On-demand RAG queries answer questions with citations
- Two types of RAG:
- Group knowledge bases - Community conversations, FAQs, support threads
- Dynamic inventory - Constantly updated data (tokens in DexGuru, points of interest in Trip Planner)
Value:
- Knowledge bases that update themselves (no manual curation)
- Context-aware answers with source attribution
- Scheduled digests keep lurkers engaged
Example: Community bot ingests 1000+ messages/day, generates weekly digests, answers questions with citations from group history.¶
3. Main Use Cases (Out of the Box)¶
3.1 Knowledge Base Management with Streamed Data¶
What: Self-updating knowledge bases from Telegram groups/channels
How:
- Messages → Elasticsearch → RAG queries
- Scheduled digests ("what you missed" recaps)
- On-demand answers with citations
Value:
- No manual curation
- Always fresh
- Source attribution
3.2 Intercom-Style Assistant¶
What: Open-source support layer connecting web and Telegram
How:
- Webchatbot embedded on site
- Connects to AG-UI Gateway (AG-UI Protocol)
- Escalates to Telegram support group
- Admins respond; replies delivered back to user
Value:
- Deflect support tickets
- Unified support across channels
- Self-hosted, no vendor lock-in
3.3 Tools Applied to Messages¶
What: Search, RAG, scheduled LLM, image processing, Whisper
How:
- Messages trigger tool execution
- Results fed back to LLM or user
- Tools configurable via LangGraph or custom code
Value:
- Rich interactions (not just text)
- Automated processing (digests, summaries)
- Extensible (add your own tools)
3.4 Comprehensive Dialog/Automated Workflows¶
What: Pre-set workflows with conditions, forks, forms, tools
How:
- BPMN workflows define user journeys — Example BPMN | Example Forms
- Forms engine renders interactive forms
- Task lists orchestrate user/LLM/automated actions
- LLM personas customize agent behavior - Example Workflow with config.yaml
Value:
- Predictable results (not "prompt and hope")
- Business logic in workflows (not code)
- Testable, version-controlled scenarios
4. Technical Stack¶
4.1 Core Framework¶
- GURU Framework - Battle-tested infrastructure (search, evals, guardrails)
- Camunda BPMN - Workflow orchestration engine (engine-api) - Modeler
- LangGraph - AI layer (agentic workflows, tools, knowledge bases)
- Elasticsearch - Dynamic RAG engine (StatefulSet)
- Redis - Session and context store (StatefulSet)
- PostgreSQL - Primary database (via PgBouncer, StatefulSet)
- ClickHouse - Event bus and analytics (StatefulSet)
- RabbitMQ - Async workloads and external tasks (StatefulSet)
4.2 Stateless Microservices (Kubernetes Deployments)¶
- bot-app - Telegram bot + AG-UI Gateway (Python)
- webchatbot-app - AI assistant for web (CopilotKit + AG-UI Protocol)
- engine-api - BPMN workflow engine (Camunda 7)
- flowapi-api - Auth, app config, analytics API
- warehouse-api - WebSocket event stream
- Workers - External Task Workers (RabbitMQ consumers)
4.3 Stateful Infrastructure (Kubernetes StatefulSets)¶
- PostgreSQL (via PgBouncer) - Primary database for engine-api and flowapi-api
- ClickHouse - Event bus and analytics storage
- Redis - Cache and state machine (Sentinel or Cluster mode)
- RabbitMQ - Async workloads (quorum queues)
- Elasticsearch - Knowledge base search (multi-node cluster)
4.4 Infrastructure¶
- Kubernetes - Container orchestration (namespaces per application)
- Docker - Containerization
- PgBouncer - PostgreSQL connection pooling
- WebSocket - Real-time notifications (warehouse-api)
- Service Mesh - Internal-only communication
4.5 Blockchain¶
- Solana Web3.js - On-chain lookups
- Wallet integration - Phantom, Solflare, Backpack
- Token gating - Wallet-based access control
5. Examples & Resources¶
5.1 BPMN Workflows & Forms¶
Community Onboarding Example:
- BPMN Workflow — Complete onboarding process with forms and conditions
- Form Examples - Sample forms for bot verification, start flow, and success states
- Start Form
- Bot Verification Form
- Bot Success Form
- Community Bot Success Form
- Community Onboarding README - Documentation and setup guide
Tools:
- Camunda Modeler — Visual BPMN editor for creating and editing workflows
5.2 Workflow Dialog Scenarios¶
Atlas Onboarding Workflow:
- Workflow Configuration — YAML configuration for agent personas, skills, and tools
- Workflow README - Complete workflow documentation
- Sales Flow Pitch - Narrative-driven onboarding example
5.3 Open Source Projects¶
- Camunda BPMN Platform - Workflow orchestration engine
- AG-UI Protocol - Unified interface protocol for AI agents
- LangGraph - AI layer for agentic workflows
- Elasticsearch - Search and analytics engine for RAG
6. Development Workflow¶
6.1 Quick Start¶
- Launch via wizard - https://atlas.gurunetwork.ai/launcher
- Get env vars -
/admincommand in bot - Fork repo - Switch to your own infrastructure
- Develop locally -
./run_development.sh - Deploy - Push to your fork, update k8s configs
6.2 Customization¶
- Workflows - Edit BPMN diagrams (Modeler) or YAML - Example BPMN | Example Workflow
- Personas - Edit Context.md + YAML - Example Config
- Tools - Add LangGraph tools or custom code
- Forms - Define in BPMN or generate with AI - Example Forms
- UI - Customize webchatbot, admin portal
6.3 Best Practices¶
- Start simple - Basic bot + RAG (
camunda_enabled=false) - Add workflows - Enable Camunda for orchestration
- Version control - Workflows, personas, configs in git
- Test locally - Use
run_development.shagainst deployed infra - Iterate - Deploy, test, customize, repeat
7. Roadmap¶
7.1 Current (v0)¶
- ✅ Dynamic RAG from streamed data
- ✅ Intercom-style webchatbot
- ✅ Basic workflows (Camunda optional)
- ✅ Launcher wizard
- ✅ AG-UI Protocol compatibility
7.2 Next (v1)¶
- 🔄 Advanced workflows (multi-step, conditional)
- 🔄 Custom tools marketplace
- 🔄 Enhanced analytics (warehouse API)
- 🔄 Cross-community features (Atlas Network)
7.3 Future (v2)¶
- 📋 Multi-project workflows
- 📋 Advanced agent personas (multi-agent systems)
- 📋 Richer MCP/A2A tools
- 📋 Enterprise features (SSO, audit logs, compliance)
Summary¶
Atlas is more than a chatbot framework - it's a complete orchestration platform for building AI-driven applications.
Key Innovations:
- Dynamic RAG — Self-propelling knowledge bases from streamed data
- Agentic Workflows - Comprehensive scenarios with forms, tools, and business logic
- One-Click Deployment - Launcher wizard spins up complete applications in minutes
- Portable Infrastructure - Fork repo, switch infra, keep developing
Use Cases: - Open-source Intercom for your service - Chatbot with comprehensive workflows - Gamification and community engagement - Community knowledge management
Get Started: - Launch your bot: https://atlas.gurunetwork.ai/launcher - Read the docs: https://atlas.gurunetwork.ai/docs - Fork the repo: https://github.com/evahteev/sol-atlas - Join the community: https://t.me/SolanaAtlas
Built on the GURU Framework • Powered by LangGraph • Connected by Solana