Architecture Overview¶
Technical deep dive into the Atlas platform architecture — understanding how components, data flows, and infrastructure work together.
System Overview¶
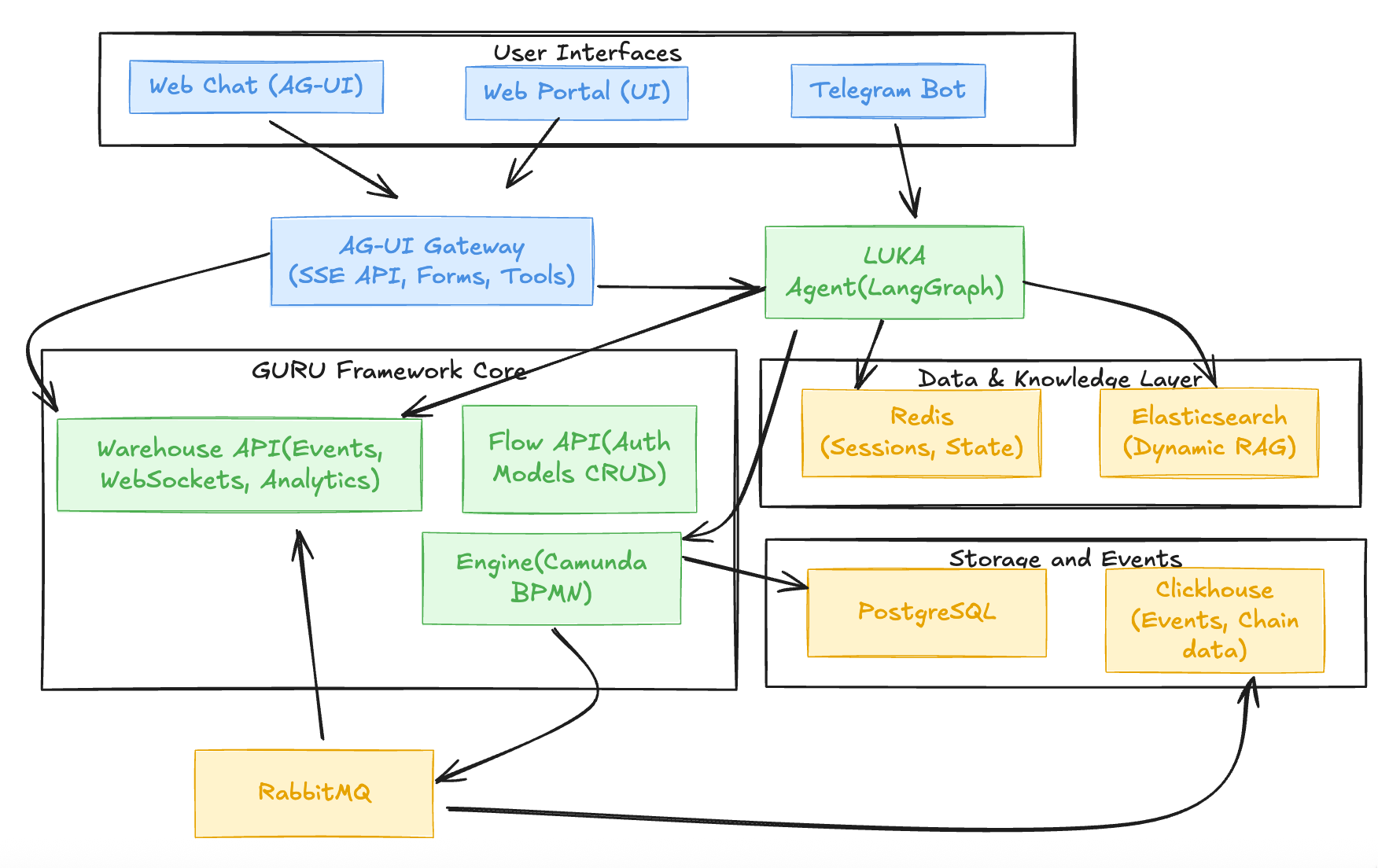
Atlas is a modular AI + Automation + Web3 orchestration platform that runs across Kubernetes. It consists of stateless microservices and stateful infrastructure components working together to provide:
- Dynamic RAG — Self-propelling knowledge bases from streamed data
- Agentic Workflows — Comprehensive scenarios with forms, tools, and business logic
- Multi-Interface Support — Telegram bot, web chat, and web UI
- One-Click Deployment — Launcher wizard for Kubernetes namespaces
Dynamic RAG: Self-Propelling Knowledge Bases¶
The Innovation: Knowledge bases that update themselves from streamed data.
How It Works:
- Ingestion - Messages from Telegram groups/channels stream into Elasticsearch
- Indexing - Embeddings generated, semantic search enabled
- Retrieval - RAG queries search Elasticsearch for relevant context
- Generation - LLM answers with citations and source attribution
Two Types of RAG:
- Group Knowledge Bases
- Source: Telegram groups, channels, Discord exports
- Use case: Community FAQs, support threads, discussions
-
Example: "How do I check my transaction?" → Answers from group history
-
Dynamic Inventory
- Source: Constantly updated data (tokens, POIs, events)
- Use case: Real-time information that changes frequently
- Example: DexGuru token inventory, Trip Planner points of interest
Benefits:
- No manual curation — knowledge bases grow organically
- Always fresh - latest messages included automatically
- Source attribution - users see where answers come from
Deployment Modes¶
Minimal Setup (Light Integration)¶
Components:
- bot-app — Telegram bot + AG-UI Gateway
- webchatbot-app — AI assistant for web
- engine-api — BPMN workflow engine (Camunda 7)
- flowapi-api — Auth, app config, analytics API
- warehouse-api — WebSocket event stream
- Redis — Cache and state management
- PostgreSQL — Primary database (via PgBouncer)
- Elasticsearch — Knowledge bases
Use Cases: - Community bots - Lightweight AI chat widgets - Basic onboarding flows
Configuration:
- camunda_enabled=false — Run without Camunda (basic bot + RAG only)
- camunda_enabled=true — Full orchestration (workflows, forms, tasks)
Enterprise / Full Deployment¶
Additional Components: - Atlas WEB UI - Comprehensive quests, Finanaces and gamefication platform - ClickHouse — Event bus and analytics - RabbitMQ — Async workloads and external tasks - Workers — External Task Workers (RabbitMQ consumers) - Multi-node clusters for stateful components
Use Cases: - Production deployments with high traffic - Advanced analytics and event processing - Complex workflows with async processing
Component Architecture¶
Stateless Microservices (Kubernetes Deployments)¶
bot-app (Telegram Bot + AG-UI Gateway)¶
Purpose: Primary interface for Webchatbot/Telegram users with integrated AG-UI Gateway
Key Features:
- Telegram/Webchatbot integration and message handling
- Onboarding flows - Example BPMN | Example Forms
- Knowledge base search (Elasticsearch)
- BPMN form rendering (from Camunda engine) - Modeler
- Inline keyboards, reply buttons, suggestions
- Wallet integration
- Quest progress tracking
Built-in moderation
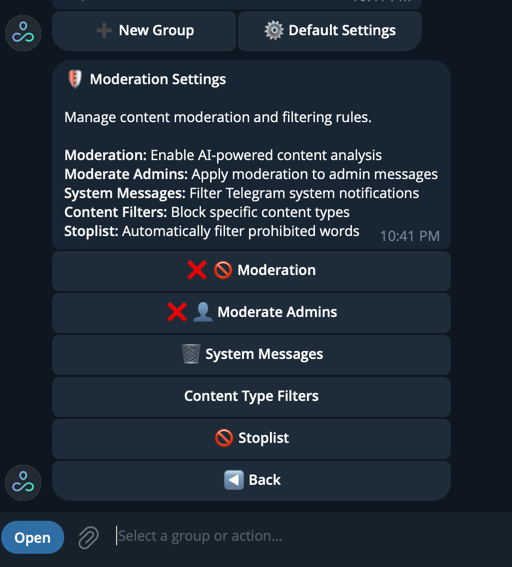
- Out-of-the-box group moderation features:
- Stopwords filtering — Automatically filter or flag messages containing prohibited words
- System messages — Automated responses and notifications for group events
- Content type controls — Filter or manage links, attachments, media, and other message types
Connections:
- Redis — User state and session management
- FlowAPI - Authentication and app configuration
- EngineAPI - BPMN workflow orchestration (Camunda)
- Elasticsearch - Knowledge base RAG queries
- warehouse-api - Real-time event notifications (WebSocket)
Deployment: Stateless Kubernetes Deployment (horizontally scalable via HPA)
webchatbot-app¶
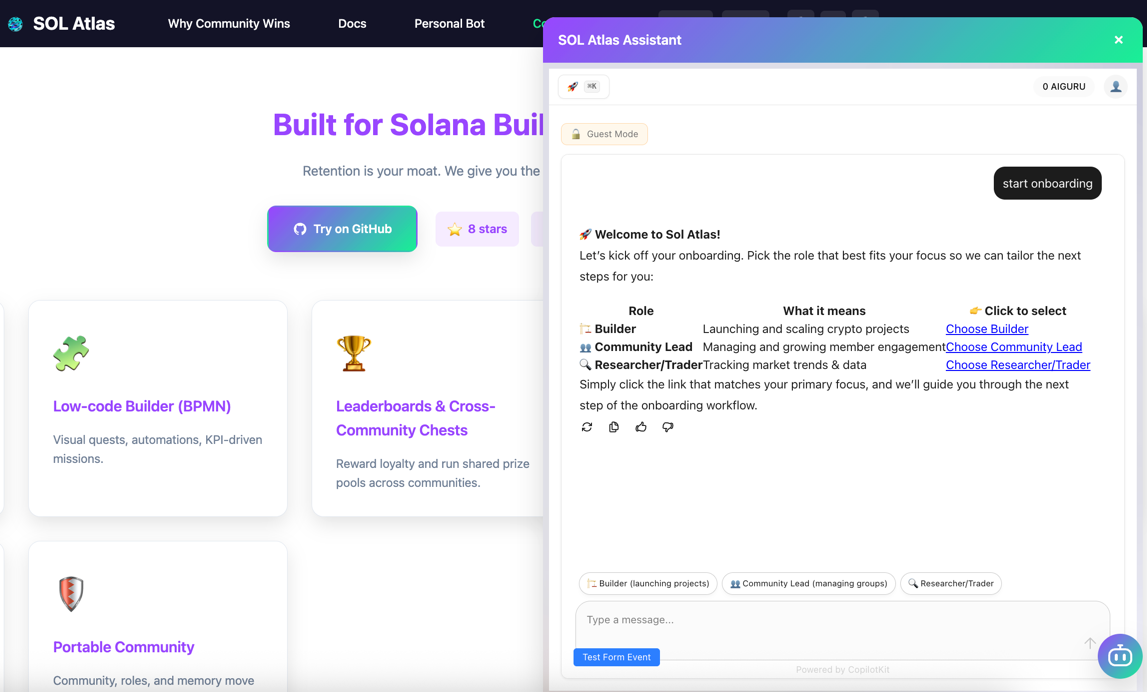
Purpose: Intercom-style AI chat widget for web
Key Features:
- Embeddable chat interface (AG-UI Protocol compatible)
- Real-time responses via AG-UI Gateway
- Forms and tool execution
- Shared context with Telegram bot
Connections:
- AG-UI Gateway (within bot-app) — Unified backend
- Redis - Session management
Deployment: Stateless Kubernetes Deployment (horizontally scalable via HPA)
engine-api (Camunda BPMN Engine)¶
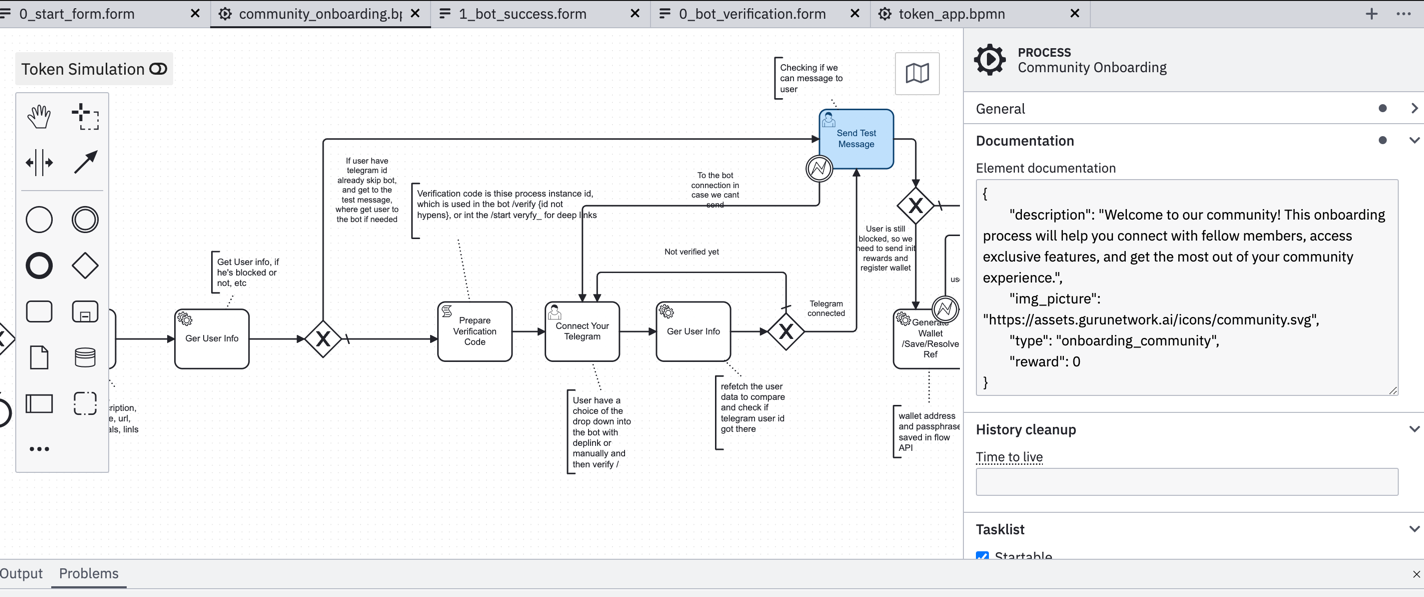
Purpose: Business process automation and workflow orchestration - Camunda BPMN Platform | Modeler
Key Features:
- Executes BPMN workflows — Example BPMN
- Visual workflows (BPMN diagrams or text/YAML) - Example Workflow
- Forms engine (generated or Camunda forms) - Example Forms
- Task lists (user, LLM, automated actions)
- External tasks (dispatched via RabbitMQ)
- Event-driven triggers
Data Storage:
- PostgreSQL (via PgBouncer) — Runtime state and process definitions
- ClickHouse - Historical events and analytics
Workflow Types:
- User workflows — Onboarding, quests, multi-step forms
- LLM workflows - Agentic scenarios with conditions and forks
- Automated workflows - Scheduled tasks, event-driven automation
Deployment: Stateless Kubernetes Deployment (horizontally scalable via HPA)
flowapi-api¶
Purpose: Authentication, app configuration, and analytics API
Key Features:
- Auth layer (JWT-based)
- Application configurations
- Analytics API
- User management
Data Storage:
- PostgreSQL (via PgBouncer) — Users, apps, configurations
- Redis - Cache and session data
Usage:
- Bot authenticates via FlowAPI
- Web UI fetches app configs
- Analytics queries user engagement metrics
Deployment: Stateless Kubernetes Deployment (horizontally scalable via HPA)
warehouse-api¶
Purpose: Event warehouse and real-time notifications
Features:
- WebSocket interface for real-time events
- Pushes updates to clients from engine events
- Historical event storage (ClickHouse)
- Analytics queries (event aggregation, dashboards)
Use Cases:
- Bot receives WebSocket notifications for new tasks
- Web UI shows real-time updates
- Analytics dashboards query historical events
Deployment: Stateless Kubernetes Deployment (horizontally scalable via HPA)
Workers (External Task Workers)¶
Purpose: Async workload processing
Features:
- External task workers (RabbitMQ consumers)
- Off-chain computation
- LLM tasks
- Long-running async actions
- Workflow integrations
Deployment: Stateless Kubernetes Deployments (horizontally scalable via HPA)
Stateful Infrastructure (Kubernetes StatefulSets)¶
PostgreSQL (Primary Database)¶
Purpose: Primary database for runtime state and configurations
Used By:
- engine-api → BPMN runtime state and process definitions
- flowapi-api → Users, apps, auth, configurations
Access: Exclusively via PgBouncer for connection pooling
Scaling: Vertical scaling or HA setup
Backup: pgBackRest
Deployment: Kubernetes StatefulSet
ClickHouse (Event Bus & Analytics)¶
Purpose: Event storage and analytics
Stores: - Engine events (from Camunda) - FlowAPI analytics - Engagement metrics - Quest/event logs
Scaling: Shards + replicas
Backup: ClickHouse backups
Deployment: Kubernetes StatefulSet
Redis (Cache + State Machine)¶
Purpose: User sessions, bot context, cache, and state management
Used By:
- bot-app — User state and session management
- flowapi-api — Cache for app configs and user data
- webchatbot-app — Session management
Use Cases:
- User session state (conversation history)
- Bot/LLM context (persona, skills, tools)
- User preferences (language, timezone, notifications)
- Temporary data (form inputs, workflow state)
- Cache layer for frequently accessed data
Benefits:
- Fast access (sub-millisecond)
- Expiration policies (auto-cleanup)
- Pub/Sub for real-time updates
Scaling: Redis Sentinel or Cluster mode
Backup: Optional snapshots
Deployment: Kubernetes StatefulSet (Redis Sentinel or Cluster mode)
RabbitMQ (Async Workloads)¶
Purpose: Message queue for async processing
Handles: - External tasks (from Camunda engine) - LLM jobs - Long-running async actions - Workflow integrations
Scaling: Quorum queues
Backup: Queue definitions backup
Deployment: Kubernetes StatefulSet
Elasticsearch (Knowledge Base Search)¶
Purpose: Searchable knowledge base from streamed data (Dynamic RAG) - Elasticsearch
Used By:
- bot-app — Knowledge base search for Telegram bot
- AG-UI Gateway (within bot-app) - Knowledge base search for webchatbot
Data Flow:
- Messages/Agentic articacts → Elasticsearch (indexed with embeddings)
- RAG queries → Elasticsearch (semantic search)
- Results → LLM (with citations)
- Answers → User (with source attribution)
Configuration:
- Index mappings for messages, documents, metadata
- Embedding models (configurable)
- Freshness scoring (recent messages ranked higher)
Scaling: Multi-node cluster
Backup: ES snapshots
Deployment: Kubernetes StatefulSet (multi-node cluster for production)
LLM Personas & Context¶
The Innovation: Agents with customizable personas, skills, and contexts (not just prompts).
How It Works:
- Context.md - Natural language persona description
- YAML config - Skills, tools, guardrails, examples
- Runtime context - User history, session state, workflow state
Example Context.md:
# Atlas Support Agent
You are a helpful support agent for Atlas, a community platform on Solana.
Your skills:
- Answer questions about Atlas features
- Help users set up their bots
- Escalate complex issues to the team
Your tools:
- search_knowledge_base (Elasticsearch RAG)
- check_user_profile (Redis)
- create_support_ticket (Flow API)
Your guardrails:
- Never share API keys or secrets
- Always cite sources when using RAG
- Escalate if user is frustrated
Benefits:
- Consistent agent behavior
- Easy customization (edit Context.md + YAML)
- Testable personas (version control, A/B testing)
Forms Engine¶
Purpose: Rich interactive forms in bot and web
Two Types:
- Camunda Forms - Defined in BPMN, rendered by engine - Example Forms | Modeler
- AI-Generated Forms - Created on-the-fly by LLM based on workflow context
Features:
- Text inputs, dropdowns, checkboxes, file uploads
- Validation rules
- Conditional fields
- Inline buttons and suggestions (bot)
- Web form rendering (AG-UI Gateway)
Example:
# BPMN form definition
form_fields:
- id: "user_name"
type: "text"
label: "What's your name?"
required: true
- id: "user_email"
type: "email"
label: "Email address"
validation: "email"
- id: "user_preference"
type: "select"
label: "Preferred language"
options: ["English", "Spanish", "French"]
Tools & Integrations¶
Built-in Tools:
- Search — Elasticsearch RAG queries
- RAG - Knowledge base retrieval with citations
- Scheduled LLM - Automated digests, summaries
- Image processing - OCR, generation, analysis (requires Camunda)
- Whisper - Voice transcription
- On-chain lookups - Solana address/tx/program data
Custom Tools:
- Add your own tools via LangGraph
- Integrate with external APIs
- Create workflow-specific tools
Data Flow¶
End-to-End Flow Example¶
- User sends
/startto bot -
bot-appreceives message via Telegram Bot API -
bot-app fetches state from Redis
-
Retrieves user session and context
-
bot-app authenticates via FlowAPI
-
JWT-based auth, app configuration
-
bot-app triggers BPMN process via EngineAPI
-
Starts workflow instance
-
Engine writes to Postgres, emits events to ClickHouse
-
Runtime state stored, events logged
-
Workers run async steps
-
External tasks consumed from RabbitMQ
-
warehouse-api pushes events to bot/webchatbot
- WebSocket notifications for real-time updates
Dynamic RAG Flow¶
- Ingestion — Messages from Telegram groups/channels stream into Elasticsearch
- Indexing — Embeddings generated, semantic search enabled
- Retrieval — RAG queries search Elasticsearch for relevant context
- Generation — LLM answers with citations and source attribution
Cross-Service Communication¶
Internal Service Mesh¶
- JWT-based auth — Service-to-service authentication
- Internal-only — Services not exposed externally
- Vault/K8s Secrets — Secure credential management
Communication Patterns¶
- REST APIs — Synchronous requests (FlowAPI, EngineAPI)
- WebSocket — Real-time events (warehouse-api)
- Message Queue — Async processing (RabbitMQ)
- Direct DB Access — Via PgBouncer (PostgreSQL)
Scaling Guidelines¶
Stateless Services¶
- Horizontally scaled via HPA (Horizontal Pod Autoscaler)
- Load balanced via Kubernetes Service
- Stateless design — No local state, all state in Redis/Postgres
Stateful Services¶
- PostgreSQL — Scale vertically or HA setup
- ClickHouse — Shards + replicas
- Elasticsearch — Multi-node cluster
- Redis — Sentinel or cluster mode
- RabbitMQ — Quorum queues
Security Model¶
- Internal-only service mesh — Services not exposed externally
- JWT-based auth — Service-to-service authentication
- Vault/K8s Secrets — Secure credential management
- Namespace isolation — Each application in its own Kubernetes namespace
- Network policies — Restrict inter-pod communication
Backup & Recovery¶
- pgBackRest — PostgreSQL backups
- ClickHouse backups — Event data
- ES snapshots — Elasticsearch knowledge bases
- Redis snapshots — Optional (ephemeral data)
- RabbitMQ definitions — Queue configurations
Kubernetes Architecture¶
Each application is deployed in its own Kubernetes namespace with:
- Isolated resources — CPU, memory limits
- Security policies — Network policies, RBAC
- Service mesh — Internal-only communication
- Monitoring — Health checks, metrics, logs
Launcher Wizard automates namespace creation and component deployment.
Next Steps¶
- Read the Components Guide for detailed component documentation
- Check the Requirements for system requirements
- Learn about the Launcher Wizard for deployment